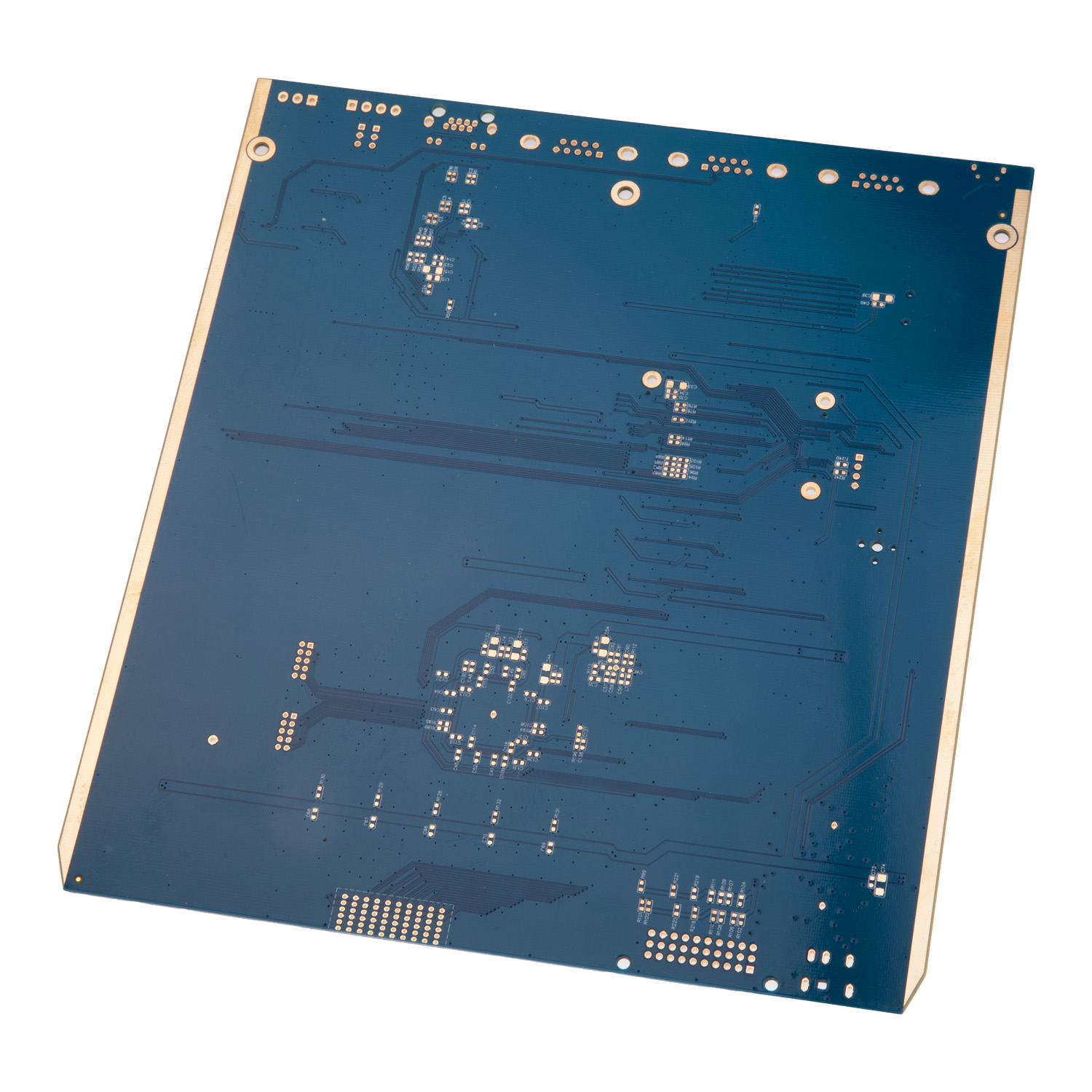
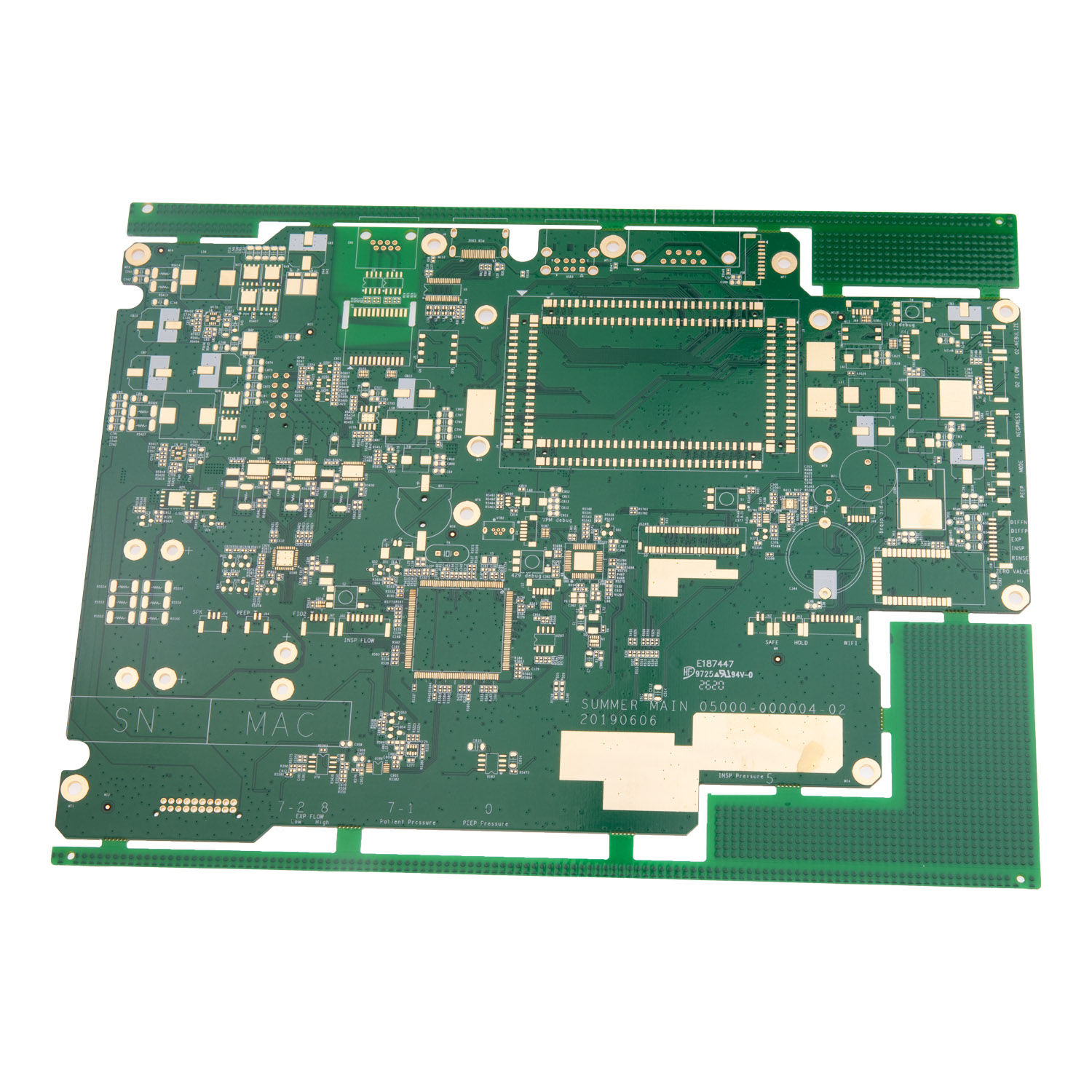
The advancement of electronic devices has placed a significant demand on the capabilities of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Among the most prominent options are rigid and multilayer printed boards, which have emerged as essential components in modern circuit design. These PCBs are reshaping the future of electronics, offering innovative solutions for complex and high-performance applications.
Understanding Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards
Rigid printed boards are sturdy, inflexible boards commonly used in applications requiring durability and structural integrity. These boards provide a solid foundation for various electronic components and are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial equipment.
On the other hand, multilayer printed boards feature multiple layers of conductive material sandwiched between insulating layers. These boards are compact, versatile, and designed for high-density and high-speed circuits, making them ideal for advanced applications such as telecommunications, aerospace, and medical devices.

Advantages of Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards
1.Compact Design
Multilayer boards enable the integration of complex circuits within a small footprint, saving space and supporting the trend toward miniaturization in electronics.
2.Enhanced Performance
The layered structure of multilayer PCBs reduces interference and improves signal integrity, critical for high-speed applications.
3.Durability
Rigid boards excel in environments that require stability and resistance to mechanical stress.
4.Versatility
Both rigid and multilayer boards are adaptable to various industries, from consumer electronics to aerospace.
Applications Driving Their Adoption
The increasing complexity of electronic systems has driven the demand for rigid and multilayer printed boards. For instance:
Automotive: Multilayer PCBs power advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle (EV) components.
Medical: Rigid boards are used in diagnostic equipment, while multilayer boards are critical in compact medical devices.
Telecommunications: Multilayer boards support high-frequency communication devices and data transfer systems.
Challenges and Future Innovations
While these PCBs offer numerous advantages, challenges such as manufacturing complexity, higher costs, and environmental concerns must be addressed. Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and recycling processes are essential to further enhance their appeal and sustainability.
Conclusion
The future of circuit design is undoubtedly intertwined with the evolution of rigid and multilayer printed boards. Their ability to meet the growing demands of modern electronics ensures their prominence in the industry. By addressing current challenges and fostering innovation, these PCBs will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of electronic devices.