Double-Sided PCBs Demystified: Understanding Design and Applications
In the realm of electronic circuitry, double-sided PCBs stand as versatile and essential components. Yet, for many, the intricacies of their design and applications remain shrouded in mystery. In this comprehensive guide, we'll unravel the complexities of double-sided PCBs, shedding light on their design principles and exploring their diverse range of applications.
What are Double-Sided PCBs?
Double-sided PCBs, also known as double-layer PCBs, feature conductive layers on both sides of the substrate, allowing for increased circuit density and complexity. This dual-layer construction enables designers to interconnect components and create more sophisticated electronic systems compared to single-sided PCBs.
Understanding the Design Process:
Designing a double-sided PCB requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. From component placement to signal routing, every aspect plays a crucial role in the board's functionality and performance. Designers must ensure proper insulation between layers to prevent signal interference and optimize the layout for efficient assembly and testing.
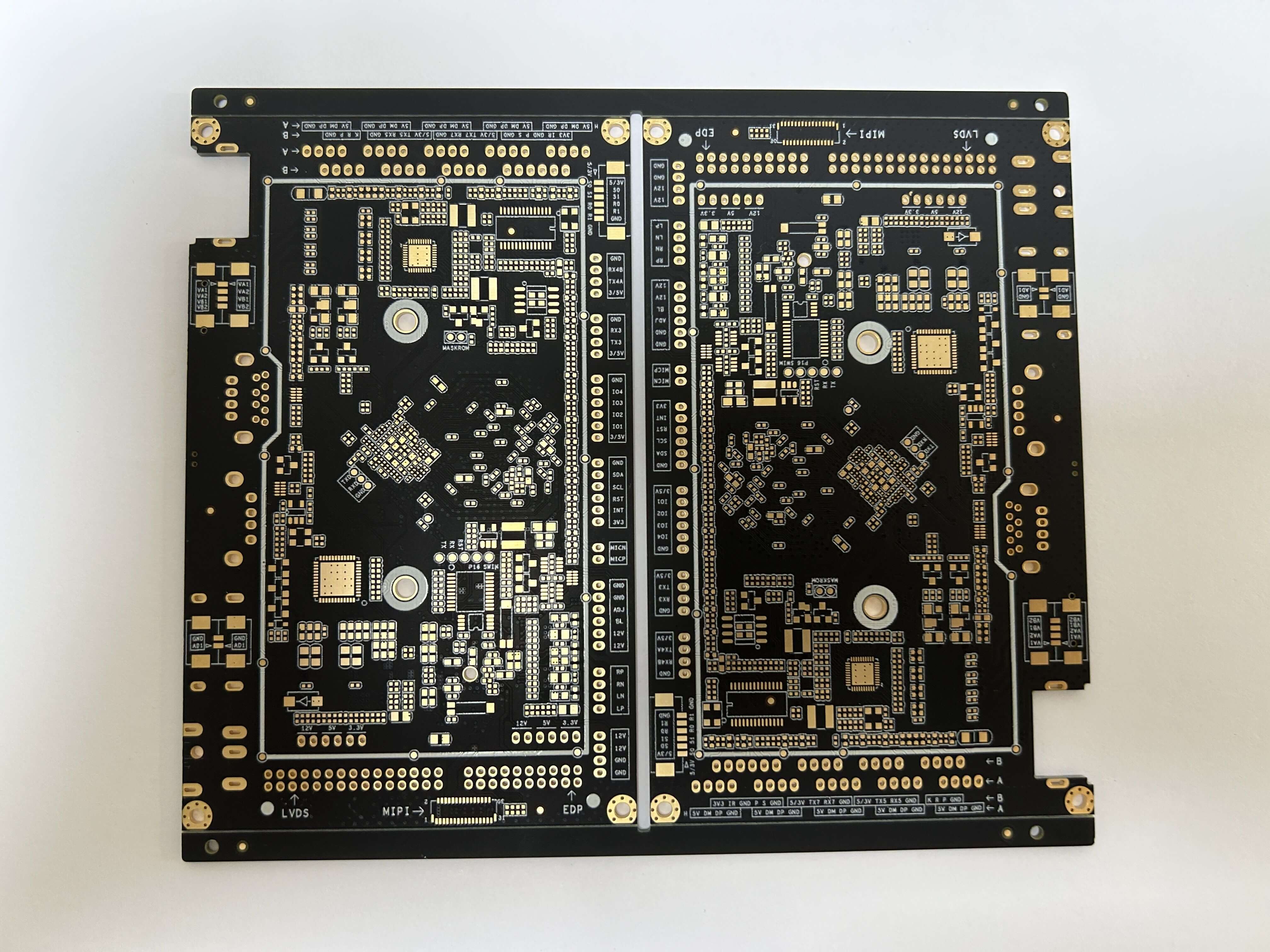
Key Design Considerations:
Several factors influence the design of double-sided PCBs, including board size, layer thickness, trace width, and spacing. By carefully balancing these parameters, designers can achieve optimal signal integrity, thermal management, and manufacturability. Additionally, the choice of materials, such as substrate and copper foil, impacts the board's electrical properties and mechanical stability.
Applications of Double-Sided PCBs:
Double-sided PCBs find applications across a wide range of industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and medical devices. They are commonly used in electronic products such as smartphones, tablets, computer peripherals, automotive infotainment systems, and industrial control systems. Their versatility makes them ideal for both simple and complex electronic designs.
Advantages of Double-Sided PCBs:
One of the primary advantages of double-sided PCBs is their ability to accommodate a higher component density, allowing for more compact and efficient designs. They also offer improved signal routing flexibility, reduced electromagnetic interference, and enhanced thermal dissipation compared to single-sided PCBs. Additionally, double-sided PCBs are often more cost-effective than multi-layer boards, making them a preferred choice for many applications.
Conclusion:
Double-sided PCBs play a crucial role in the development of modern electronic devices, offering a balance of performance, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the design principles and applications of double-sided PCBs, designers and engineers can unlock new possibilities in electronic design and innovation. Whether used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, or industrial equipment, double-sided PCBs continue to shape the future of technology.