In the world of modern electronics, the need for more compact, reliable, and efficient circuit designs is constantly growing. One of the key technologies that enable this is the double-sided printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike single-sided PCBs, double-sided PCBs offer enhanced connectivity and design flexibility, making them indispensable in many electronic applications. In this blog post, we'll explore the benefits, applications, and considerations for using double-sided PCBs in electronics.
1. What is a Double-Sided PCB?
A double-sided pcb is a type of circuit board that has conductive copper layers on both sides. This allows for components to be mounted and connections to be made on both the top and bottom of the board. The layers are interconnected through vias (holes) that enable electrical connections between the two sides.
2. Advantages of Double-Sided PCBs in Electronics
a. Increased Circuit Density:
Double-sided PCBs allow for more complex circuits to be designed in a smaller area. By utilizing both sides of the board, engineers can place more components and create more intricate designs without increasing the size of the PCB.
b. Enhanced Design Flexibility:
With the ability to route connections on both sides, double-sided PCBs provide greater flexibility in the design process. This is particularly important for advanced electronic devices where space and performance are critical.
c. Improved Signal Integrity:
Double-sided PCBs help reduce signal interference by allowing shorter and more direct routing paths for connections. This results in better signal integrity, which is essential for high-speed and sensitive electronic applications.
d. Cost-Effective Solution:
While double-sided PCBs are more complex than single-sided PCBs, they are still a cost-effective option compared to multi-layer PCBs. They strike a balance between complexity and cost, making them ideal for many electronic products.
3. Common Applications of Double-Sided PCBs
Double-sided PCBs are used in a wide range of electronic devices across various industries:
a. Consumer Electronics:
Products like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices often use double-sided PCBs to maximize functionality while maintaining a compact form factor.
b. Industrial Control Systems:
In industrial automation, double-sided PCBs are used in control panels, sensors, and other equipment that require reliable and efficient circuitry.
c. Automotive Electronics:
The automotive industry relies on double-sided PCBs for various applications, including engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
d. Communication Devices:
Routers, modems, and other communication devices benefit from the enhanced performance and reduced interference provided by double-sided PCBs.
4. Design Considerations for Double-Sided PCBs
When designing a double-sided PCB, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance:
a. Thermal Management:
With more components and connections on both sides, managing heat dissipation becomes crucial. Designers must consider the placement of heat-generating components and the use of thermal vias or heat sinks.
b. Via Placement and Design:
Vias are essential for connecting the two sides of the PCB, but their placement and size must be carefully planned to avoid signal interference and maintain structural integrity.
c. Material Selection:
The choice of materials, such as the type of substrate and copper thickness, can significantly impact the PCB's performance, durability, and cost. FR4 is a common choice for double-sided PCBs due to its excellent electrical insulation and mechanical stability.
d. Testing and Quality Control:
Double-sided PCBs require rigorous testing to ensure all connections are functioning correctly and that there are no shorts or open circuits. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing are commonly used for quality control.
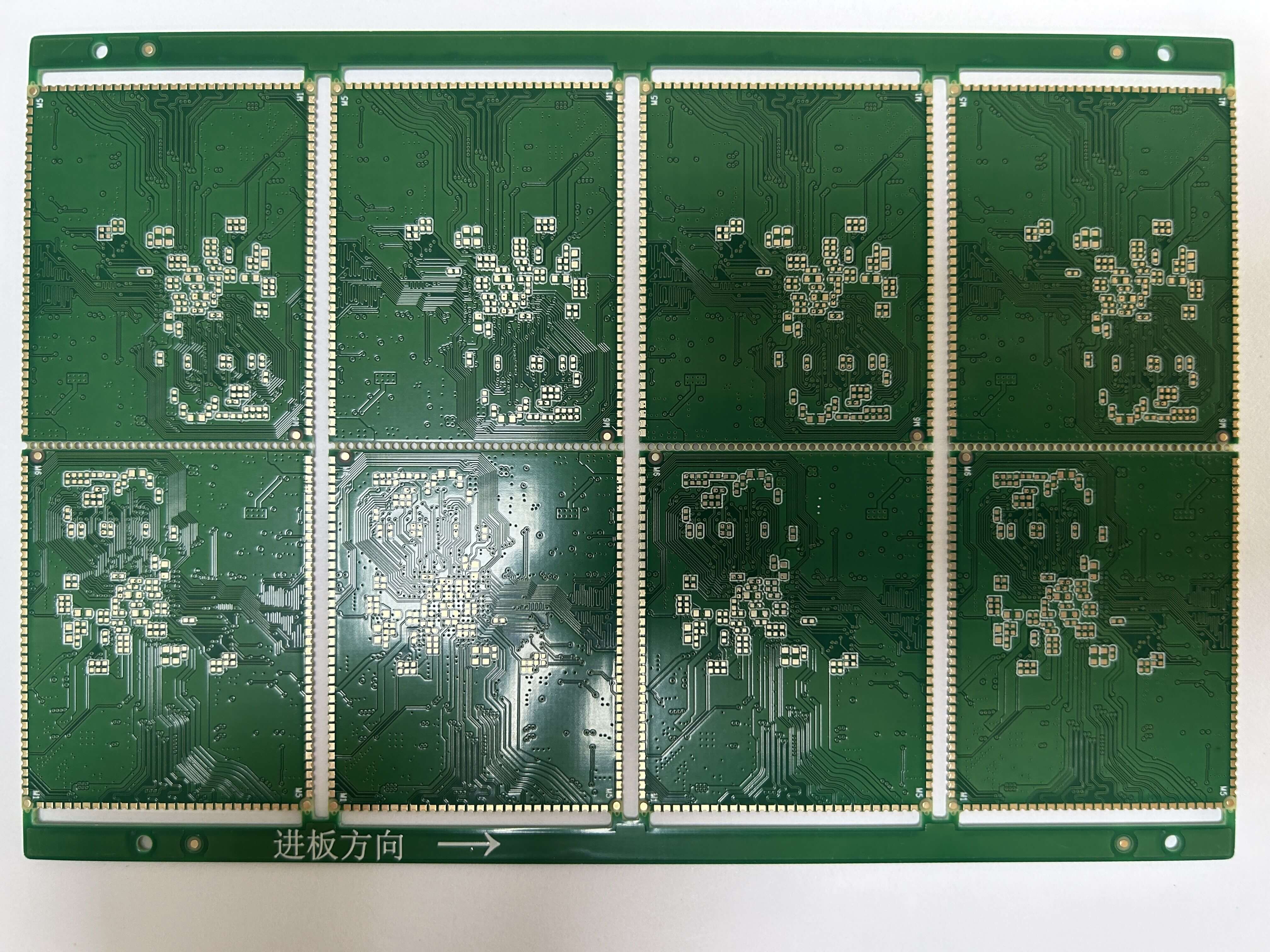

5. Conclusion
Double-sided pcbs play a crucial role in the development of modern electronic devices. Their ability to offer increased circuit density, design flexibility, and improved performance makes them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Whether you're designing consumer electronics, industrial systems, or automotive components, understanding the benefits and considerations of double-sided PCBs will help you create more efficient and reliable products.
If you're looking to incorporate double-sided PCBs into your next project, consider working with a reputable manufacturer who can provide high-quality, customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. By doing so, you'll be well-equipped to take advantage of this versatile and powerful technology in your electronic designs.